| Prepared at the 74th JECFA (2011) and published in FAO JECFA Monographs 11 (2011), superseding the specifications prepared at the 63rd JECFA (2004), published in the Combined Compendium of Food Additive Specifications, FAO JECFA Monographs 1 (2005). A group ADI ”not specified” for modified celluloses (ethyl cellulose, ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, methyl ethyl cellulose, and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose) was established at the 35th JECFA (1989). | |
| SYNONYMS | INS No. 464 |
| DEFINITION | Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose is a methyl cellulose modified by treatment with alkali and propylene oxide by which a small number of 2-hydroxypropyl groups are attached through ether links to the anhydroglucose units of the cellulose. The article in commerce may be further specified by viscosity. |
| Chemical names | Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose, 2-hydroxypropyl ether of methyl cellulose |
| C.A.S. number | 9004-65-3 |
| Chemical formula | [C6H7O2(OH)x(OCH3)y(OCH2CHOHCH3)z]n wherez = 0.07 – 0.34y = 1.12 – 2.03x = 3-(z + y): (z + y = degree of substitution) |
| Structural formula |  where R = H or CH3 or CH2CHOHCH3 |
| Formula weight | Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14.Structural unit with 1.19 degree of substitution: approx. 180.Structural unit with 2.37 degree of substitution: approx. 210.Macromolecules: from about 13,000 (n about 70) up to about 200,000 (n about 1000) |
| Assay | Not less than 19% and not more than 30% of methoxylgroups (-OCH3) and not less than 3% and not more than 12% hydroxypropoxyl groups (-OCH2CHOHCH3), on the dried basis |
| DESCRIPTION | Hygroscopic white or off-white powder, or granules or fine fibres |
| FUNCTIONAL USES | Emulsifier, thickening agent, stabilizer |
| CHARACTERISTICS | |
| IDENTIFICATION | |
| Solubility (Vol.4) | Swells in water, producing a clear to opalescent, viscous colloidal solution; insoluble in ethanol |
| Foam formation | A 0.1% solution of the sample is shaken vigorously. A layer of foam appears. This test permits the distinction of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose from other cellulose ethers. |
| Precipitate formation | To 5 ml of a 0.5% solution of the sample, add 5 ml of a 5% solution of copper sulfate or of aluminium sulfate. No precipitate appears. This test permits the distinction of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose from other cellulose ethers. |
| Substituents | See description under METHOD OF ASSAY |
| PURITY | |
| Loss on drying | Not more than 10% (105o to constant weight) |
| pH | Not less than 5 and not more than 8 (1 in 100 soln) |
| Sulfated ash | Not more than 1.5% for products with viscosities of 50 centipoises or above, and not more than 3% for products with viscosities below 50 centipoisesTest 1 g of the sample |
| Propylene chlorohydrins | Not more than 0.1 mg/kgSee description under TESTS |
| Lead | Not more than 2 mg/kgDetermine using an AAS/ICP-AES technique appropriate to the specified level. The selection of sample size and method of sample preparation may be based on the principles of the methods described in Volume 4 (under “General Methods, Metallic Impurities”). |
| TESTS | |
| PURITY TESTS | |
| Propylene chlorohydrins | Determine by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) (Vol. 4) using the following procedure.Note: Propylene chlorohydrins (PCH) are present as 2 isomers namely: 1-chloro-2-propanol (1C2P) and 2-chloro-1-propanol (2C1P). Internal standard solutionsInternal Standard Stock Solution #1 (1 mg/ml): Weigh 0.1 g to nearest 0.1 mg (approximately 100 μl) of o-xylene-d10 (CAS 56004-61-6) into a 100 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with methanol.Internal Standard Stock Solution #2 (100 μg/ml): Pipette 5ml of Internal Standard Stock Solution #1 into a 50 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with methanol.Internal Standard Stock Solution #3 (4 μg/ml): Pipette 1 ml of Internal Standard Stock Solution #2 into a 25 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with methanol:Internal Standard Solution #4 (16 ng/ml): Add 1 ml of Internal Standard Stock Solution #3 into a 250 ml volumetric flask and dilute to volume with diethyl ether.Internal Standard Solution #5 (8 ng/ml): Pipette 25 ml of Internal Standard Stock Solution #4 into a 50 ml volumetric flask and dilute to volume with diethyl ether.Standards Stock Standard Solution #1 (1mg/ml): Weigh 0.1 g to the nearest 0.1 mg of propylene chlorohydrin, mixture of 1-Chloro-2-propanol-75% and 2-Chloro-1-propanol-25%, Eastman Kodak, Cat. # P1325 or equivalent) into a 100 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with diethyl ether.Stock Standard Solution #2 (100 μg/ml): Pipette 5 ml of Standard Stock Solution #1 into a 50 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with diethyl etherStock Standard Solution #3 (10 μg/ml): Pipette 5 ml of Standard Stock Solution #2 into a 50 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with diethyl ether.Stock Standard Solution #4 (500 ng/ml): Pipette 5 ml of Standard Stock Solution #3 into a 100 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with diethyl ether.Note: All standard solutions should be prepared with diethyl ether of the highest purity available.Prepare working standard solutions by pipetting the volumes shown in the table below in to a 10 ml volumetric flask and make up to volume with diethyl ether. 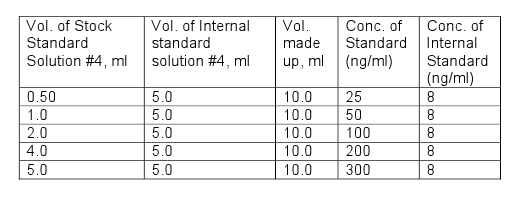 Instrument:A gas chromatograph with a mass selective detector (GCMS) in Selective Ion Monitoring (SIM) mode, Electron impact ionisation (EI) source, pulsed-splitless injector and a data station.GCMS Conditions:Inlet temperature 225° Pulse pressure 50 psi until 2 min Inlet purge flow 40 ml/min at 2 min Injection volume 5 μlGuard ColumnDeactivated fused silica, 10 m x 0.25 mm i.d. x 0.35 mm o.d. Column 30 m x 0.25 mm i.d. x 1.4 μm film DB-624 or equivalentTemperature programming:Initial temperature 40° Initial hold Time 5.0 min Ramp rate 10°/min Temperature 2 80° Hold time 3.0 min Ramp rate 25°/min Final temperature 230° Final hold time 5.0 min Carrier:Gas Helium Flow rate 1.4 ml/min Column head pressure 11.5 psiDetector:Ion source temperature. 230° Transfer line temperature 260° SIM ions:o-Xylene-d10 Target ion m/z = 116, Qualifier ion m/z = 98 1-Chloro-2-Propanol Target ion m/z = 79, Qualifier ion m/z = 81 2-Chloro-1-Propanol Target ion m/z= 58, Qualifier ion m/z= 31 Retention times:o-Xylene-d10 13.7 min 1-Chloro-2-Propanol 9.5 min 2-Chloro-1-Propanol 10.4 min Procedure: Weigh about 1.00 g, to nearest 0.1 mg, of sample into a glass vial. Pipette 5.0 ml of Internal Standard Solution #5 into the vial, securely close the vial and sonicate for 10 minutes. Centrifuge the vial to separate the mixture. Remove a portion of the diethyl ether layer for GCMS analysis. Calculations: Calculate the ratios of detector responses for 1C2P and 2C1P versus detector response for o-xylene-d10 at each working standard concentration using the following equation: AR(std) = R(std)/R(IS)whereAR(std) is the ratio of detector response for 1C2P or 2C1P versus the detector response for o-xylene-d10 in the standard; R(std) is the detector response of the target ion for 1C2P or 2C1P in the standard; and R(IS) is the detector response of the target ion for o-xylene-d10 in the standard. Prepare standard curves for 1C2P and 2C1P by plotting the concentration of 1C2P or 2C1P (ng/ml) versus the ratios of detector response (AR(std)) for each isomer in the working standards. Calculate the ratio of detector response for 1C2P and 2C1P versus the detector response for o-xylene-d10 in the sample using the following equation:AR(sample) = R(Sample)/R(IS)where AR(sample) is the ratio of detector response for 1C2P or 2C1P versus the detector response for o-xylene-d10 in the sample; R(sample) is the detector response of the target ion for 1C2P or 2C1P in the sample; and R(IS) is the detector response of the target ion for o-xylene-d10 in the sample. From the linear regression of the standard curves for each isomer, calculate ng/g using the following equation: ng/g = (V x (AR(sample) -b)/m)/W where AR(sample) is the Ratio of detector response for 1C2P or 2C1P versus the detector response for o-xylene-d10 in the sample; b is the y-intercept of the linear regression curve; m is the slope of the linear regression curve; V is the final volume (5.0 ml); and W is the weight of the sample in grams. Report the PCH content in mg/kg as the sum of the 2 isomers (1C2P and 2C1P). |
| METHOD OF ASSAY | Determination of the hydroxypropoxyl groupApparatusThe apparatus for hydroxypropoxyl group determination is shown in the accompanying diagram. The boiling flask, D, is fitted with an aluminium foil-covered Vigreux column, E, on the sidearm and with a bleeder tube through the neck and to the bottom of the flask for the introduction of steam and nitrogen. A steam generator, B, is attached to the bleeder tube through Tube C, and a condenser, F, is attached to the Vigreux column. The boiling flask and steam generator are immersed in an oil bath, A, equipped with a thermo-regulator such that a temperature of 155o and the desired heating rate may be maintained. The distillate is collected in a 150-ml beaker, G, or other suitable container. ProcedureTransfer about 100 mg of the sample, previously dried at 105o for 2 h and accurately weighed, into the boiling flash, and add 10 ml of chromium trioxide solution (60 g in 140 ml of water). Immerse the steam generator and the boiling flask in the oil bath (at room temperature) to the level of the top of the chromium trioxide solution. Start cooling water through the condenser and pass nitrogen gas through the boiling flask at the rate of one bubble per sec. Starting at room temperature, raise the temperature of the oil bath to 155o over a period of not less than 30 min, and maintain this temperature until the end of the determination. Distil until 50 ml of the distillate is collected. Detach the condenser from the Vigreux column, and wash it with water, collecting the washings in the distillate container. Titrate the combined washings and distillate with 0.02 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 7.0, using a pH meter set at the expanded scale.NOTE: Phenolphthalein TS may be used for this titration, if it is also used for all standards and blanks.Record the volume, Va of the 0.02 N sodium hydroxide used. Add 500 mg of sodium bicarbonate and 10 ml of dilute sulfuric acid TS, and then after evolution of carbon dioxide has ceased, add 1 g of potassium iodide. Stopper the flask, shake the mixture, and allow it to stand in the dark for 5 min. Titrate the liberated iodine with 0.02 N sodium thiosulfate to the sharp disappearance of the yellow colour, confirming the end-point by the addition of a few drops of starch TS. Record the volume of 0.02 N sodium thiosulfate required as Ya.Make several reagent blank determinations, using only the chromium trioxide solution in the above procedure. The ratio of the sodium hydroxide titration (Vb) to the sodium thiosulfate titration (Yb), corrected for variation in normalities, will give the acidity-to-oxidizing ratio, Vb/Yb= K, for the chromium trioxide carried over in the distillation. The factor K should be constant for all determinations.Make a series of blank determinations using 100 mg of methyl-cellulose (containing no foreign material) in place of the sample, recording the average volume of 0.02 N sodium hydroxide required as Vm and the average volume of 0.02 N sodium thiosulfate required as Ym. Calculate the hydroxypropoxyl content of the sample, in mg, by the formula:75.0 x [N1 (Va-Vm) – k N2 (Ya – Ym)]whereN1 = the exact normality of the 0.02 N sodium hydroxide solutionN2 = the exact normality of the 0.02 N sodium thiosulfate solutionk = VbN1/YbN2 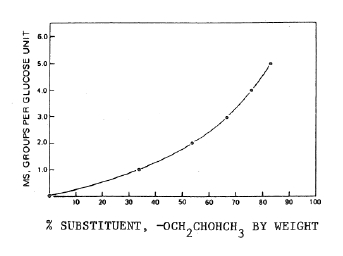 Chart for converting percentage of substitution, by weight, of hydroxypropoxyl groups to molecular substitution per glucose unit.Determination of the methoxyl groupVolume 4, under ASSAY METHODS, Cellulose Derivatives Assay, Ethoxyl and Methoxyl Group Determination. See Apparatus and Procedure in Ethoxy and Methoxy Group Determination and determine the content of methoxy groups (-OCH3). CalculationCalculate as percentage. Correct the % of methoxy groups thus determined by the formula:A – (B x 0.93 x 31 / 75)whereA is the total % of -OCH3 groups determined; B is the % of -OCH2CHOHCH3 determined in the Method of Assay for hydroxypropoxy group content; and 0.93 is an average obtained by determining, on a large number of samples, the propylene produced from the reaction of hydriodic acid with hydroxypropoxy groups during the Method of Assay for methoxy groups (-OCH3). A – (B x 0.93 x 31 / 75)whereA = the total % of -OCH3 groups determinedB = the % of -OCH2CHOHCH3 determined in the Method of Assay for Hydroxypropoxyl group content0.93 = an average obtained by determing, on a large number of samples, the propylene produced from the reaction of hydriodic acid with hydroxypropoxyl groups during the Method of Assay for metoxyl groups (-OCH3). |
CyberColloids
