| Prepared at the 55th JECFA (2000) and published in FNP52 Add 8 (2000), superseding specifications prepared at the 51st JECFA (1998) and published in FNP 52 Add 6 (1998). An ADI “Not specified” was established at the 49th JECFA (1998). | |
| SYNONYMS | Cellulose gel; INS No. 460(i) |
| DEFINITION | Purified, partially depolymerized cellulose prepared by treating alphacellulose, obtained as a pulp from fibrous plant material, with mineral acids. The degree of polymerization is typically less than 400. Not more than 10% of the particles have a diameter below 5 μm. |
| Chemical names | Cellulose |
| C.A.S. number | 9004-34-6 |
| Chemical formula | (C6H10O5)n |
| Assay | Not less than 97% of carbohydrate calculated as cellulose on the dry basis. |
| DESCRIPTION | Fine, white or almost white, odourless, free flowing crystalline powder. |
| FUNCTIONAL USES | Emulsifier, stabilizer, anticaking agent, dispersing agent |
| CHARACTERISTICS | |
| IDENTIFICATION | |
| Solubility (Vol.4) | Insoluble in water, ethanol, ether and dilute mineral acids. Slightly soluble in sodium hydroxide solution |
| Infrared absorption | The infrared absorption spectrum of a potassium bromide dispersion of the sample corresponds to the infrared spectrum below. |
| Suspensoid | Mix 30 g of the sample with 270 ml of water in a high-speed (18,000 rpm) blender for 5 min. Transfer 100 ml of the mixture to a 100-ml graduated cylinder, and allow to stand for 3 h. A white, opaque, bubble-free dispersion that forms a supernatant, is obtained. |
| PURITY | |
| Loss on drying (Vol.4) | Not more than 7.0% (105 o, 3 h) |
| pH (Vol.4) | 5.0 – 7.5Shake 5 g of the sample with 40 ml of water for 20 min and centrifuge. Determine the pH of the supernatant. |
| Sulfated ash (Vol.4) | Not more than 0.05%Test 10 g of the sample (Method I) |
| Water solubleSubstances | Not more than 0.24%.Shake 5 g of the sample with approximately 80 ml of water for 10 min, filter through Whatman No. 42 or equivalent filter paper into a tared beaker, wash residue with 20 ml of water and evaporate to dryness on a steam bath. Dry at 105o for 1 h., cool, weigh and calculate as percentage. |
| Starch | Not detectableTo 20 ml of the dispersion obtained in the identification test for starch, add a few drops of iodine TS, and mix. No purplish to blue or blue colour should be obtained. |
| Lead (Vol.4) | Not more than 2 mg/kgDetermine using an AAS/ICP-AES technique appropriate to the specified level. The selection of sample size and method of sample preparation may be based on principles of methods described in Volume 4 (under “General Methods, Metallic Impurities”). |
| METHOD OF ASSAY | Transfer about 125 mg of the sample, accurately weighed, to a 300 ml Erlenmeyer flask, using about 25 ml of water. Add 50.0 ml of 0.5N potassium dichromate and mix. Carefully add 100 ml of sulfuric acid and heat to boiling. Remove from heat, allow to stand at room temperature for 15 min and cool in a water bath. Transfer the contents into a 250 ml volumetric flask, rinse flask with distilled water, add rinsings to the volumetric flask and dilute with water almost to volume. Allow the volumetric flask to reach room temperature (25o), then make up to volume with water and mix. Titrate a 50.0 ml aliquot with 0.1N ferrous ammonium sulfate using 2 or 3 drops of ortho-phenanthroline TS as the indicator and record the volume required as S in ml. Perform a blank determination and record the volume of 0.1N ferrous ammonium sulfate required as B in ml. Calculate the percentage of cellulose in the sample by the formula:(B – S) x (338 / W)%Where: W is the weight of sample taken, in mg, corrected for loss on drying. |
| Infrared Spectrum | 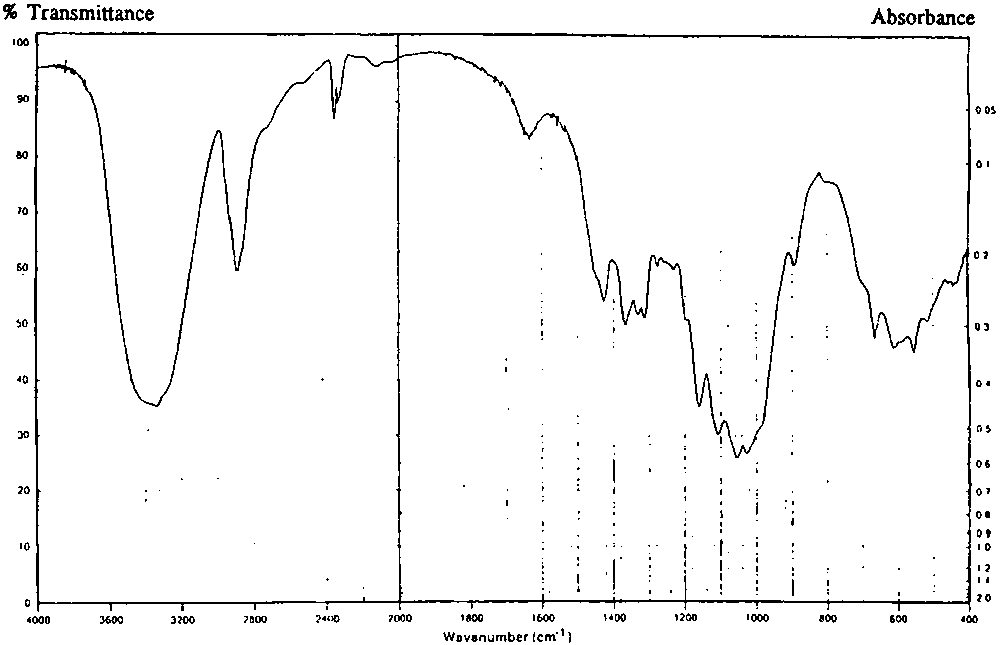 |
CyberColloids
